Band Warm Up #1
3 x 10 reps
Lateral band walks
Banded lunge with rotation (R/L)
Banded rows
Banded standing press
Toy soldiers
Walking knee hugs
WOD
For time:
SB G2S10
30 DB devils press
SB G2S10
30 DB thrusters
SB G2S10
30 DB devils press
SB G2S10

Band Warm Up #1
3 x 10 reps
Lateral band walks
Banded lunge with rotation (R/L)
Banded rows
Banded standing press
Toy soldiers
Walking knee hugs
WOD
For time:
SB G2S10
30 DB devils press
SB G2S10
30 DB thrusters
SB G2S10
30 DB devils press
SB G2S10
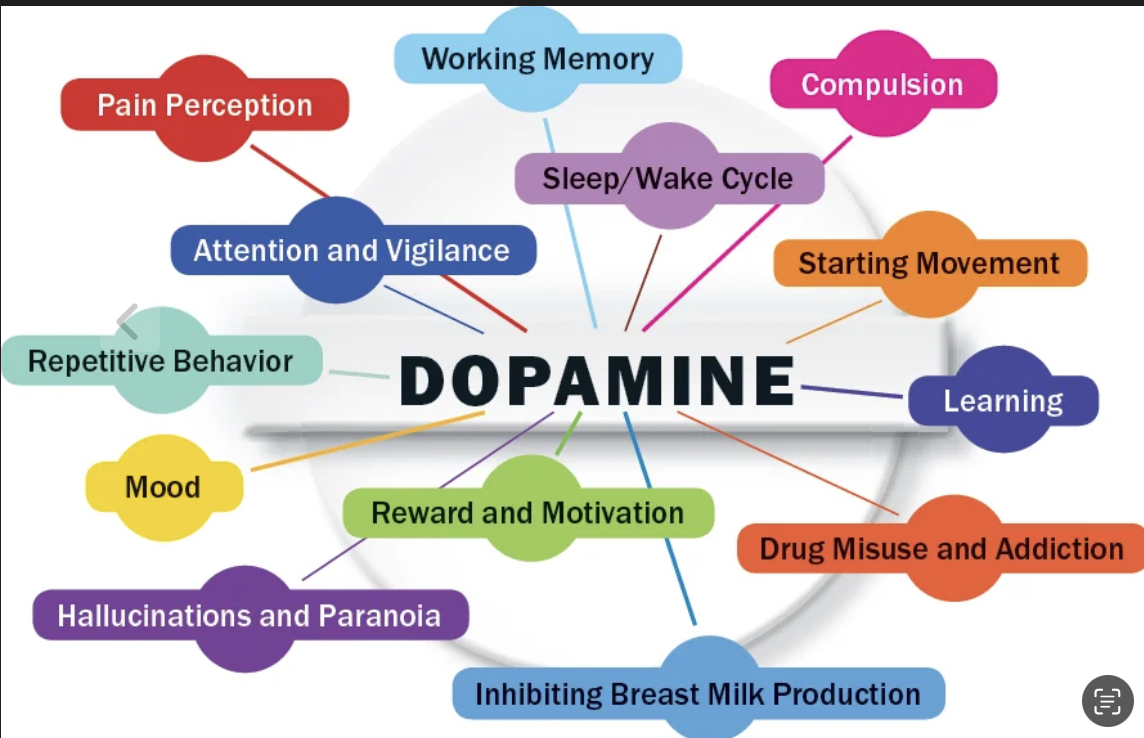
There’s a reason we light up after a morning run, feel a rush of satisfaction after completing a tough workout, or get a boost from a deep conversation or heartfelt goal. The common thread? Dopamine.
Often misunderstood as just the "pleasure chemical," dopamine is more accurately our motivation molecule—and recent science shows that it's also a critical player in healthy aging.
Dopamine isn’t just about feeling good. It governs movement, focus, learning, decision-making, and reward-seeking behavior. These functions are deeply linked to our ability to sustain healthy habits, engage in physical activity, and even resist the pull of harmful behaviors—all of which directly affect how long and how well we live.
For Coach Ray Traitz, understanding dopamine’s role in behavior and performance has transformed the way he coaches clients. Rather than forcing willpower, Ray helps people engineer their environments and habits to naturally reinforce better decisions—and ultimately, better health.
Dr. Huberman explains that dopamine isn’t just triggered by achieving a goal—it spikes during the pursuit. This insight has powerful implications for fitness and longevity:
Embrace the process – Learn to link dopamine to effort, not just outcome.
Limit artificial spikes – Avoid overuse of social media or sugar that hijack dopamine.
Use novelty strategically – Try new workouts or challenges to sustain dopamine motivation.
Dr. Sinclair connects dopamine to cellular health and longevity:
Dopamine supports mitochondrial function, which powers our cells.
Movement increases dopamine and activates longevity pathways (like AMPK and sirtuins).
Mindset matters – Positive outlooks, often reinforced by healthy dopamine, lower stress and inflammation markers.
McGonigal highlights how physical activity boosts dopamine, which in turn reinforces the behavior:
Group workouts increase dopamine through connection.
Anticipation of movement is a dopamine trigger—use pre-workout rituals.
Celebrate small wins—this reinforces consistency and builds neural resilience.
The 5-Minute Rule Experiment (Huberman Lab)
Participants who paired small tasks (like 5-minute walks or cold showers) with a mindset of effort-based reward saw an increase in dopamine signaling. This led to consistent habit formation and decreased reliance on stimulants like caffeine.
Longevity Study on Movement and Dopamine (Sinclair Group)
Mice genetically predisposed to short lifespans experienced a 30% increase in longevity when exposed to short daily bursts of exercise. The mechanism? Enhanced dopamine feedback loops that boosted mitochondrial efficiency.
Community Fitness and Neurochemistry (McGonigal Research)
In a longitudinal study of adults ages 40–65, those in group fitness classes reported 2.4x higher motivation levels and 35% better adherence to exercise regimens—linked to shared dopamine boosts and mutual accountability.
Coach Ray doesn’t just preach discipline—he engineers momentum. Through a careful blend of:
Daily movement rituals
Strength-based training goals
Habit stacking to boost dopamine naturally
Mindset coaching to reduce self-judgment
Ray helps clients build a rhythm of progress that’s dopamine-smart and life-sustaining. His programs go beyond calories and reps—they create neurochemical environments that want to keep getting better.
If you’re stuck in cycles of burnout, inconsistency, or stress-based training, it’s time to work smarter. By leveraging the science of dopamine, Coach Ray can help you retrain your brain and body for sustainable vitality.
Whether you're new to fitness or looking to fine-tune your long-term health, Ray Traitz offers personalized coaching in strength, nutrition, and lifestyle design.
📧 Contact him at amrapfitness@hotmail.com
Huberman, A. (2022). Using Dopamine to Drive Motivation, Focus & Satisfaction. Huberman Lab Podcast.
Sinclair, D. (2019). Lifespan: Why We Age—and Why We Don't Have To. Atria Books.
McGonigal, K. (2015). The Upside of Stress: Why Stress Is Good for You, and How to Get Good at It. Avery.


Robbie
Complete as many rounds as possible in 25 minutes of:
8 freestanding handstand push-ups
15-foot L-sit rope climb, 1 ascent
U.S. Army Staff Sergeant Robert J. Miller died Jan. 25, 2008, in Bari Kowt, Afghanistan, of wounds sustained when he encountered small-arms fire while conducting combat operations. The 24-year-old, of Oviedo, Florida, was assigned to the 3rd Battalion, 3rd Special Forces Group (Airborne) in Fort Bragg, North Carolina, and served during Operation Enduring Freedom. In October of 2010, Miller was awarded the Medal of Honor posthumously for his heroic actions in combat. Miller is survived by his parents, Philip and Maureen; brothers, Thomas, Martin and Edward; and sisters, Joanna, Mary, Therese and Patricia.
Core Warm Up
*Coaches choice: run/row/ jump rope
Dead bug complex
Plank complex
Gymnastic isometric holds
WOD
6x
20:30
Double unders/ taps
Mountain climbers
High knees
Burpees